What are archives?
There are many definitions of archives, but for the purposes of understanding Spydus Archives, "archives" are unpublished records — usually relating to an organisation or person — which are preserved because they are considered to have enduring value. Examples of these records may be those from a local organisation such as minutes, newsletters and/or documents about a business or sporting group. Records may also be correspondence, diaries and/or memorabilia relating to a person or family of the local community.
Each archival agency will have a different policy for determining what records are of enduring value to keep for the community they serve. Some of these reasons might be for evidential purposes, for preserving institutional and cultural memory, for personal reasons that affect the lives of the community today or for learning about the past.
How are archival resources different from library resources?
Archives have characteristics which make them very different from the books, serials, DVDs and other resources that you find in a library. We've summarized the general differences in the table below.
| Archives | Library resources |
| Unpublished | Published |
| Unique, "one-off" | Mass-produced |
| Irreplaceable | Replaceable |
| Usually ordered by context, i.e. the order in which they were created, for example, chronologically by creating agency | Usually ordered by subject, for example, Dewey Decimal System) |
| Description usually based on ISAD(G) | Description based on AACRII |
| Record where the resource came from | Record what the resource is |
| Focus on collections of records and hierarchical relationships between records, for example, Collection - Series - File - Item | Focus on individual bibliographic records |
Why use Archives?
The Archives module:
- Allows for detailed archival description using cataloguing worksheets, based on international archiving standards.
- Allows for detailed accession records using cataloguing worksheets, based on international standards.
- Authority Control allows you to create your own thesaurus of names, places, subjects and forms.
- Gives you the ability to create an entire collection separate from your library holdings.
- Allows borrowers to search from a dedicated Archives search interface, and gives the ability to integrate with bibliographic records from an All Resources search to enhance findability.
Working with records
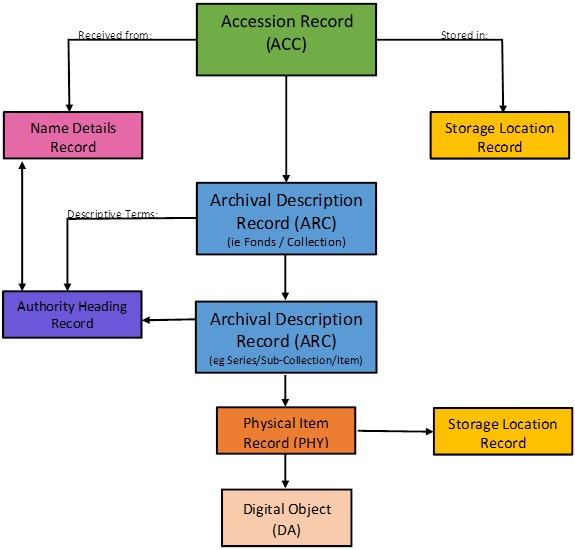
Archives includes several different record types which together support the description and management of archival resources. These include:
| Record type | Brief description |
| Accession (ACC) | For recording accessions (a bit like library acquisitions). An accession record documents when an Archive takes custody of materials and can be considered a formal record of receipt. |
| Archival description (ARC) | For describing an item or collections of items in the standard hierarchical model (multi-level). Based on ISAD(G). |
| Physical item (PHY) | For recording the physical characteristics of the item(s) which are described in the Archival Description (ARC) to which it is linked. When an ARC record is created, a linked PHY record is also created from information entered in the Holdings Area – originals. |
| Authority heading | For creating access points for the resource in the ARC record. Authority headings are divided into categories — Name, Place, Subject and Form. |
| Name details | For recording the name(s) (personal, corporate body, or family) associated with accessions or archival descriptions. The name record links to a name authority heading, and records information including biographical history, date of birth, etc. It is based on ISAAR(CPF). |
| Storage location | For indicating the location(s) where a resource is or may in the future be located. Storage location records can be setup in advance and then linked to an ACC and/or ARC record. |
These record types interrelate with each other. An example of how they interrelate is provided below.
Go to button
On the entry form for an accession record, archival description, authority, physical item, name and movement, you'll see a Go to button on the Action Menu. You can use this to quickly go to a particular area on the entry form. Click Go to and then click the field you want.
The archival management process
There are many different workflows that can be used in the Archives module. Surrounding the workflows you perform within Archives, are other archival activities which are essential to the background preparation of archive collections for accessioning and cataloguing in Archives.
If we look at the process in which each archival function would be performed, it would most likely be in the following order.
| Archival Function (in the order it would be done) | Description as it relates to the Archives module |
| Appraisal | Determining whether to add the archival materials to your collection (whether it fits in your scope of collections statement). This must be done before proceeding to the next step. |
| Accessioning | Process of recording the materials coming into the repository. Various details of the materials are collected when they are transferred into the archives, including for example: name of donor, name of the archives being received, description of the material, conditions of the deposit or access restrictions, the date received, receipt number issued to the depositor. This information can be entered as an Accession Record (ACC) in Archives. |
| Arrangement | Arranging a collection into its hierarchical original order. This involves breaking down collections into an internal hierarchical structure, e.g. Collection - Series - File - Item. Each hierarchical level will have an associated archival Description in Archives. |
| Processing and Preservation |
Includes:
The final storage location of the archives can be recorded in Archives in a Storage Location record. |
| Description | Cataloguing of the collection by creating an archival description for each level in the hierarchy. Archival description will be based on ISAD(G). The description can be entered as an Archival Description record (ARC) in Archives, while Items will be entered as a Physical record (PHY). |
| Access and Use | Includes conditions governing access and reproduction, associated finding aids etc. Access information can be recorded in Archives in the ARC record. |
| Digital Objects | Linking a digital image or document related to the Archival description. The digital object can be stored in the Digital Assets repository in Spydus or elsewhere and the Digital Asset record (DA)will be linked to the Item record (PHY) as part of this process. |
As you can see from this table, Archives can be used to record information in all steps apart from the first which requires the archivist to make a judgement against their scope of collections statement.